Technical Architecture
This page provides an overview of Bolt Liquidity's technical architecture and an in-depth look at how the product works under-the-hood.
Bolt Architecture Overview
Bolt’s architecture is purpose-built for high-quality execution and capital-efficient, cross-chain liquidity. The system is composed of three core components that work together to deliver deterministic, CEX-like pricing on-chain:
Price Oracle
Bolt Outposts
Market Makers (Order Settlers)
Each component has a distinct role, but all are tightly integrated to ensure consistent pricing, reliable execution, and efficient liquidity usage across chains.

Core Components
Price Oracle
The Bolt Price Oracle is the foundation of the protocol.
Continuously sources market data from centralized and decentralized exchanges
Incorporates liquidity depth, volume, and volatility signals
Produces deterministic reference prices used by all Bolt Outposts
A network of validators emits Proof of Price Efficiency (PoPE), verifying that execution prices reflect the best available global market rates. This effectively acts as a global quoting engine, ensuring price consistency across all supported chains.
Bolt Outposts
Bolt Outposts are chain-specific smart contracts deployed across supported ecosystems such as Cosmos and Sui.
Outposts:
Expose Bolt’s pricing and settlement logic directly on-chain
Serve as execution hubs for swaps on each chain
Integrate with wallets, aggregators, and DeFi applications
Outposts use single-sided, multi-quote liquidity pools, where liquidity providers deposit a single base asset that can be traded against multiple quote assets.
This design:
Eliminates impermanent loss
Avoids liquidity fragmentation across many trading pairs
Improves capital efficiency
Market Makers (Order Settlers)
Market Makers are responsible for fulfilling swap orders and maintaining healthy pool liquidity.
Their role includes:
Providing liquidity to Bolt Outposts
Hedging trades on external venues (typically CEXs) to remain delta-neutral
Rebalancing pools by returning hedged assets on-chain
Market Makers earn fees from:
Swap execution
Liquidity provision and pool maintenance
This incentivizes active participation and ensures consistent execution quality.

Trade & Liquidity Flow
Swap Execution Flow
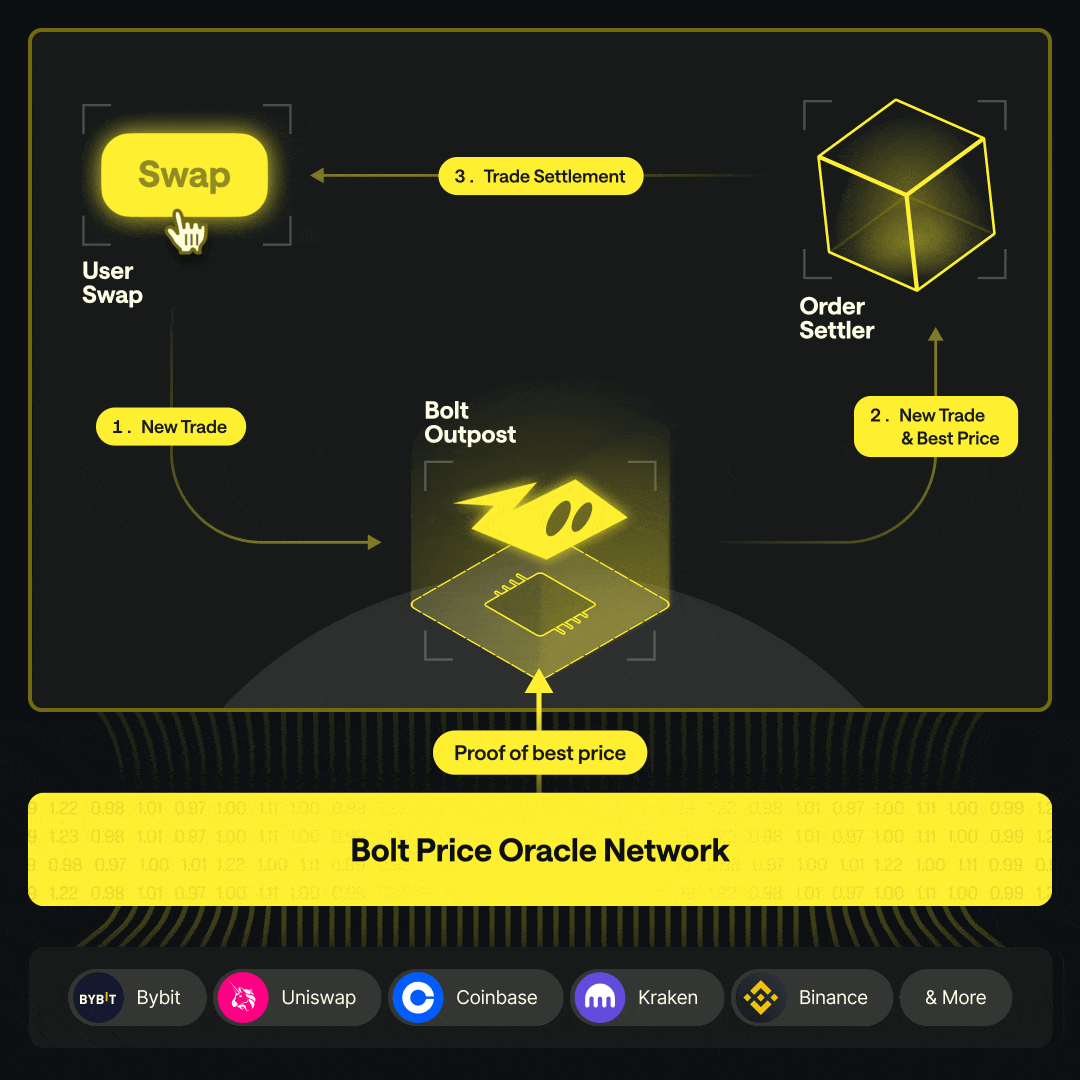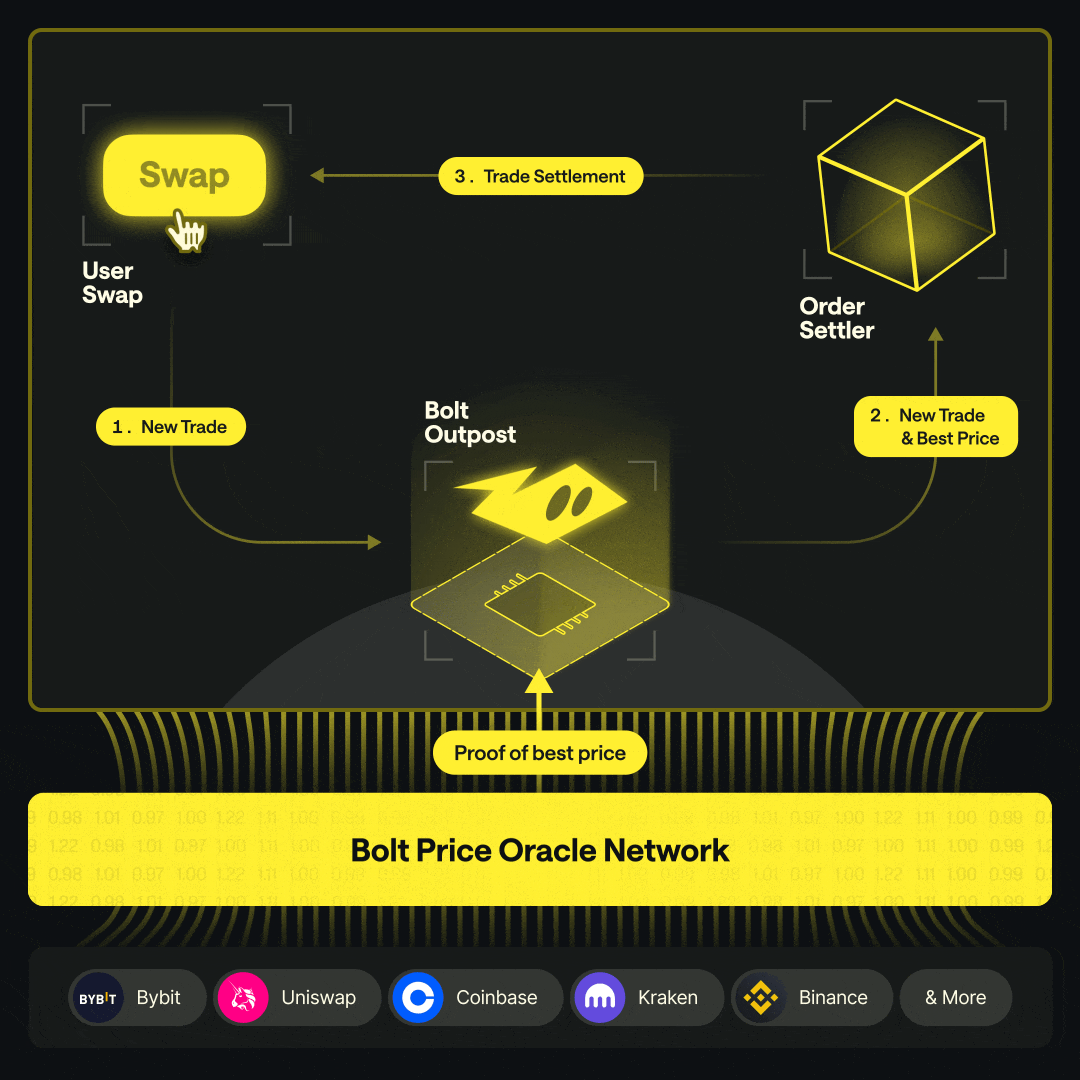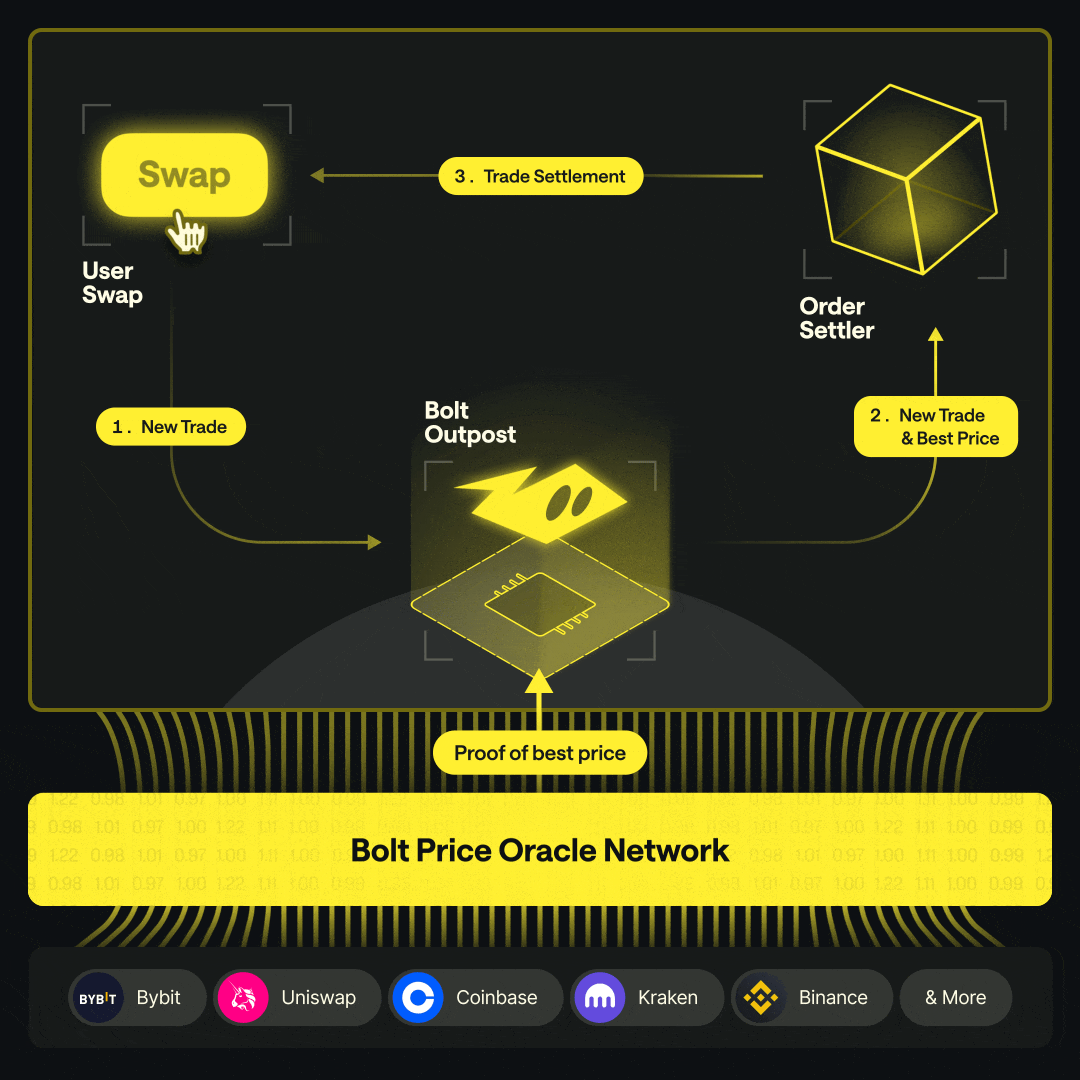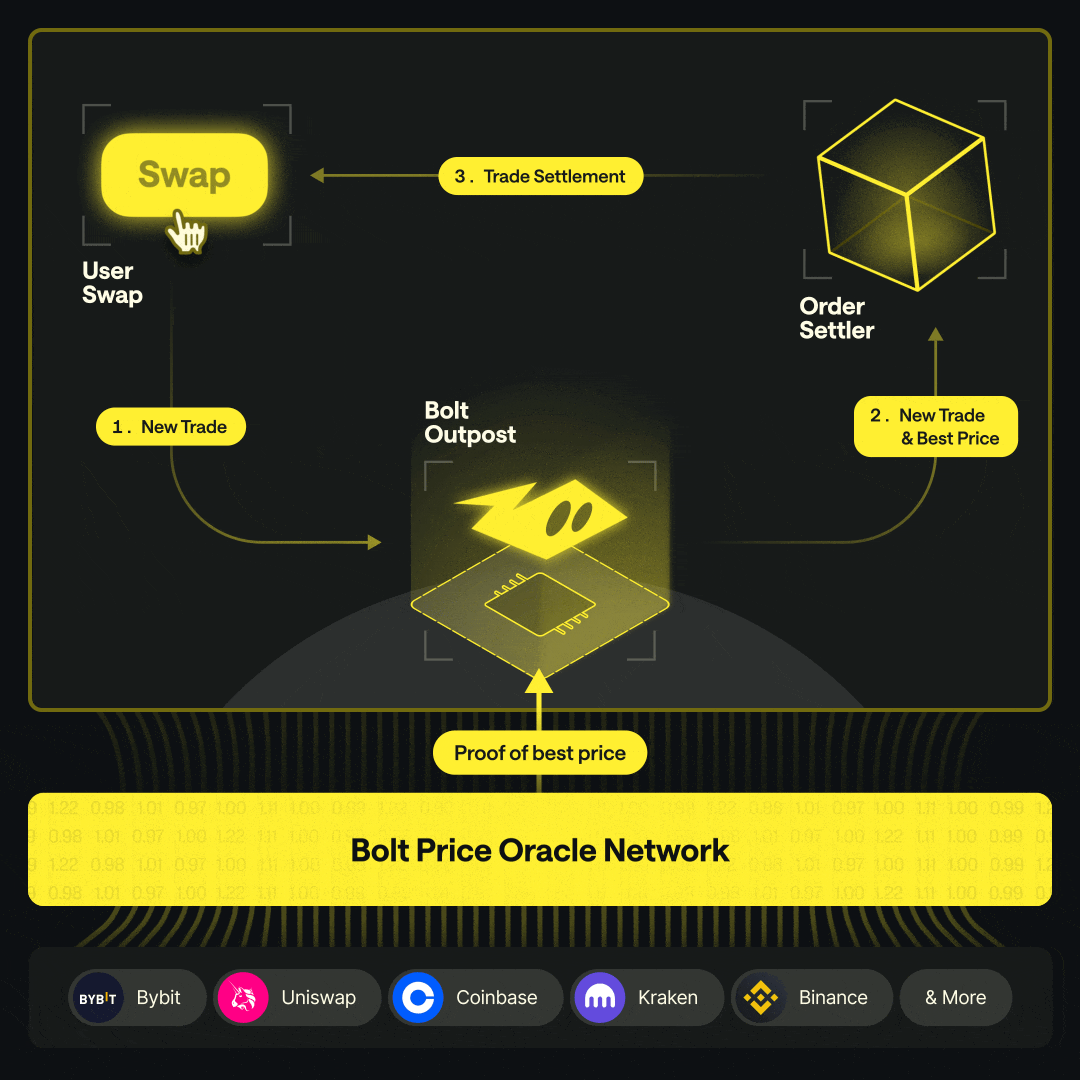
Order Creation A user initiates a swap on a Bolt Outpost at the oracle-quoted price.
On-Chain Execution The Outpost smart contract executes the swap at the validated price.
Quote assets are sent to the user
The user’s payment asset accrues in the liquidity pool
Hedging The Market Maker executes an offsetting, delta-neutral hedge on an external venue, typically repurchasing the quote asset.
Rebalancing When pool thresholds are reached, the Market Maker moves assets from the external venue back on-chain to replenish the pool.
Liquidity Lifecycle
LP Deposit – LPs deposit
baseassets into Bolt pools on the OutpostMarket Making – Market Makers use these pools to fulfill user swaps and hedge any token risk externally
Fee Accrual – Fees are distributed proportionally to LPs and Market Makers via Pool contracts, as swaps are performed Market Makers earn fees which can be withdrawn as
quoteassetsLP Withdrawal – LPs can withdraw their pool liquidity at any time, based on whatever share of the pool they own as
baseorquoteassets
Liquidity Provision
LPs are currently permissioned within Bolt during Alpha release, please contact the team via Contact & Support Channels
Last updated